Radiant Medical Centre
Antenatal Check-ups
The antenatal check-up program covers all stages of pregnancy, including early pregnancy health assessments, genetic screening, and fetal development monitoring; mid-pregnancy structural ultrasounds and gestational diabetes screening; as well as late pregnancy vaccinations and delivery preparation. The program aims to ensure the health and safety of both mother and baby.
The following is the schedule of prenatal examination:
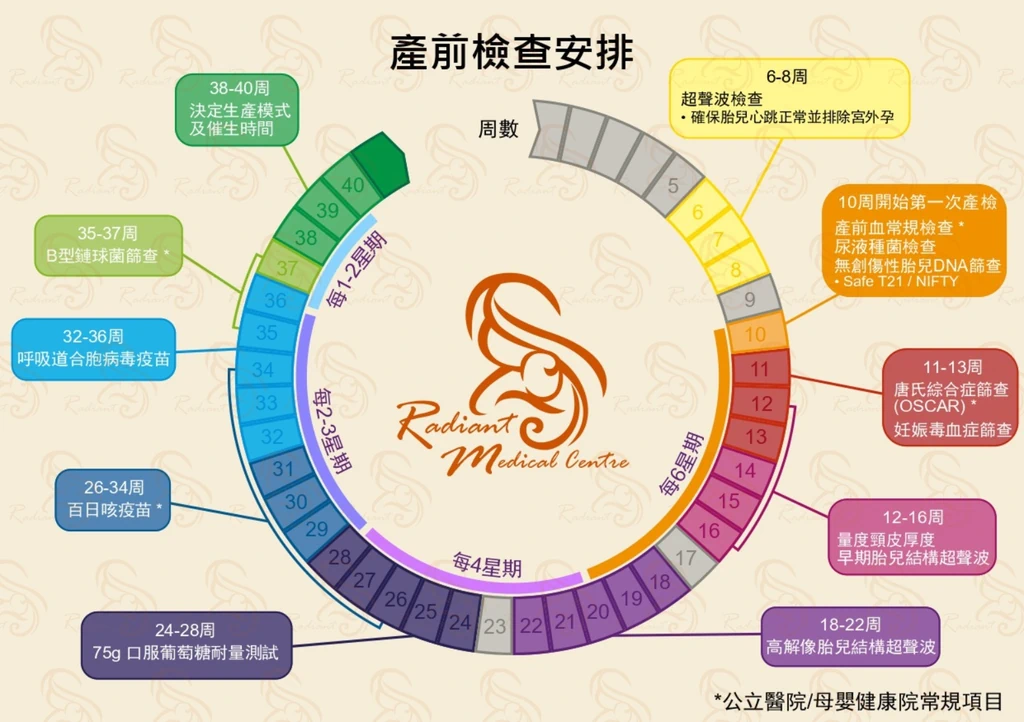
● 6–8 Weeks Ultrasound Examination: To confirm a normal fetal heartbeat, determine the gestational age, and rule out early pregnancy complications such as ectopic pregnancy.
● First Antenatal Check-up Starting at 10 Weeks
Prenatal Blood Tests: Assess the mother’s blood health, including anemia, blood type, and other hematological indicators.
Non-invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) / Cell-free Fetal DNA Screening (T21/NIFTY)(T21/NIFTY): Screens for chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) and Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18).
● 11–13 Weeks
Down Syndrome Screening (OSCAR): A combined blood test and nuchal translucency measurement to screen for fetal chromosomal abnormalities.
Pregnancy toxemia screening: assess the risk of gestational hypertension and protect the health of pregnant women.
● 12–16 Weeks
Nuchal Translucency Measurement: Ultrasound measurement of the fetal neck’s translucent layer to further assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities. (please delete this sentence, not appropriate to put here)
Early Fetal Anatomy Ultrasound: Examines the basic structural development of the fetus.
● 18–22 Weeks
High-Resolution Fetal Anatomy Ultrasound: A comprehensive examination of the fetus’s major organs, including the brain, heart, limbs, and internal organs, to detect significant structural abnormalities and ensure normal fetal development.
● 24-28 Weeks
Oral glucose tolerance test: screening for gestational diabetes to ensure stable blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
● 26–34 Weeks
Pertussis Vaccination: By receiving the pertussis vaccine, pregnant women can develop antibodies before delivery and pass them to the fetus, protecting the newborn from whooping cough infection.
● 32–36 Weeks
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccination: Helps prevent newborns from contracting severe lower respiratory tract infections caused by RSV within the first six months after birth. (please delete this part, not generally recommended)
● 35–37 Weeks
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Screening: Tests whether the mother carries Group B Streptococcus to prevent transmission to the baby during delivery.
● 38–40 Weeks
Birth Plan: Discuss delivery options with the doctor and, if necessary, arrange for induction or related procedures.

